Market downturns, like the one through the first half of 2022, could be a good time to adjust your fund portfolio to minimize the tax bite. Here’s how to calculate the best ways to do that – now and in the future.
Taxable accounts you hold longer than a year incur long-term capital gains taxes when you sell investments. You realize losses or gains, meaning your losses are subtracted from the gains and, if the result is positive, your gains are taxed at the preferable long-term capital gains rates (a rate often much less than ordinary income tax rates).
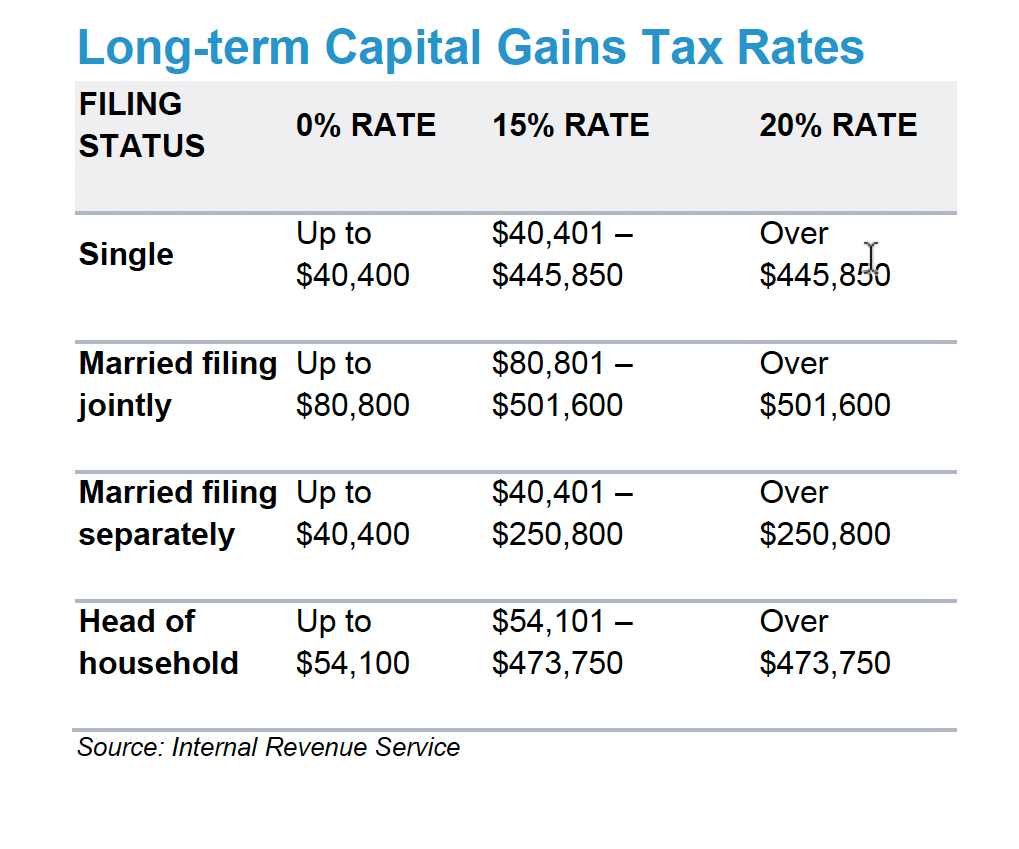
The rates range are either 0%, 15% or 20%, depending on your income.
Trimming Taxes
When your losses exceed your gains, your capital gains are netted against the losses and the losses subtracted from the gains. In this manner, your gains incur no tax. If your losses exceed gains, you can use the excess to reduce your ordinary income up to $3,000 per year ($1,500 if filing separately), carrying over any remaining losses to future years.
Let’s say your four taxable accounts (A, B, C and D) each have a cost basis (what you paid for the fund originally) of $10,000.
- Fund A’s current value is $15,000 and it gained $5,000
- Fund B’s current value is $20,000 and it gained $10,000
- Fund C’s current value is $8,000 and it lost $2,000 and
- Fund D’s current value is $4,000 and it lost $6,000.
As is, you net a gain of $7,000 (your gains of $5,000 plus $10,000, minus your losses of $2,000 and $6,000).
You can sell various combinations of your funds’ holdings, though, for best tax advantage. Selling all of funds A (which had a gain of $5,000) and D (loss of $6,000) nets you a long-term capital loss of $1,000. If this is your only activity in long-term holdings for the year, you owe no capital gains and you realize $1,000 in losses to use to reduce your income.
What if you sell just 80% of your fund B, meaning $8,000 in gain? Then you sell all of both funds C and D, which combined lost $8,000? The result: zero capital gains and zero capital gains tax.
This last example is the least efficient way to use your losses. Always attempt to maximize the amount you can use against ordinary income, resulting in the greatest tax reduction. If you sell all of funds A, C and D, for instance, you get a capital loss of $3,000 ($5,000 minus $2,000 minus $6,000) that you can use to offset income this year and potentially in future years.
These strategies become even more important with larger holdings and if you have funds that rebound in value in the future.
Social Security and Other Tax Issues
Be careful with your capital gains. For instance, a gain taxed at even the 0% rate can increase your adjusted gross income, in turn increasing taxes on your Social Security income.
Also use care after you sell a holding that recognized a loss. If you look to better your tax situation in the future with the same or a substantially similar asset, you need to wait at least 30 days before you buy. Otherwise you trigger what’s called a wash sale treatment, which according to the Internal Revenue Service, effectively eliminating that loss for tax purposes.
Copyright © 2022 FMeX. All rights reserved. Distributed by Financial Media Exchange
Important Disclosures: The opinions expressed herein are those of Ballast Advisors, LLC and are subject to change without notice. The third-party material presented is derived from sources Ballast Advisors consider to be reliable, but the accuracy and completeness cannot be guaranteed. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Nothing contained herein is an offer to purchase or sell any product. This material is for informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. Ballast Advisors reserve the right to modify its current investment strategies and techniques based on changing market dynamics or client needs. The information presented here is not specific to any individual’s personal circumstances. To the extent that this material concerns tax matters, it is not intended or written to be used, and cannot be used, by a taxpayer for the purpose of avoiding penalties that may be imposed by law. Each taxpayer should seek independent advice from a tax professional based on his or her individual circumstances. Ballast Advisors, LLC is a registered investment advisor under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended. Registration does not imply a certain level of skill or training. More information about the firm, including its services, strategies, and fees can be found in our ADV Part 2, which is available without charge upon request.


